Dehling, Barreto & Graham (2022) – Trends in Ecology and Evolution
Highlights
- Species interactions are key for maintaining biodiversity and the functioning of ecological communities.
- Despite the importance of species interactions for ecological communities, there is currently no method to quantify the contribution of individual species to maintaining functional diversity (FD) and phylogenetic diversity (PD) via their interactions with other species.
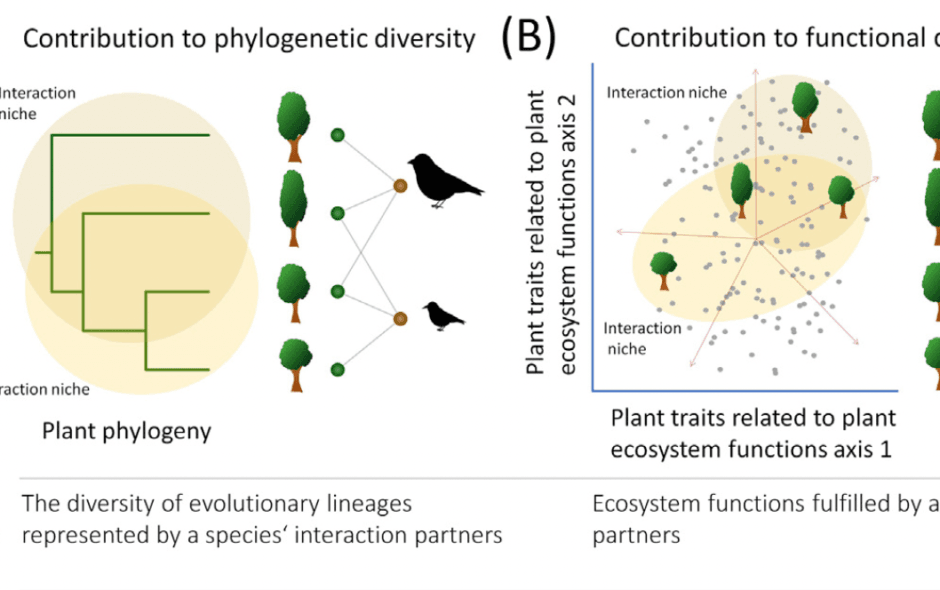
- Species’ interaction niches – the FD and PD of their interaction partners – measure the contribution of mutualists to conserving ecosystem functions and evolutionary lineages, respectively.
- Measuring the contribution of species to maintaining FD and PD via their mutualistic interactions will guide conservation efforts and facilitate new studies on the evolution of ecological communities.
Abstract
Reduction of functional diversity (FD) and phylogenetic diversity (PD) likely affects ecosystem functions and reduces the potential of communities to respond to changes, such as climate change. Mutualistic interactions are essential for maintaining diversity, but their role has largely been ignored in conservation planning. We propose using a species’ interaction niche – the diversity of its interaction partners – to measure a species’ contribution to the maintenance of FD and PD via mutualistic interactions, and thus identify species and interspecific interactions that are particularly important for the conservation of ecosystem functions and evolutionary lineages in ecological communities. Our approach represents a switch in perspective that allows a direct assessment of the importance of mutualistic interactions for the maintenance of biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2022.05.006