Graham et al. (2025) – Ecology Letters
Biodiversity Patterns Redefined in Environmental Space
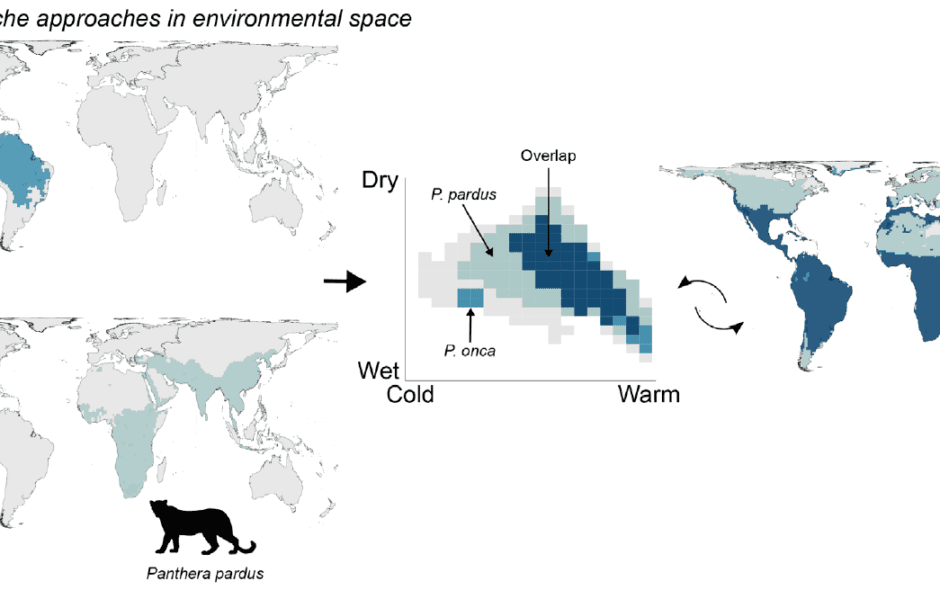
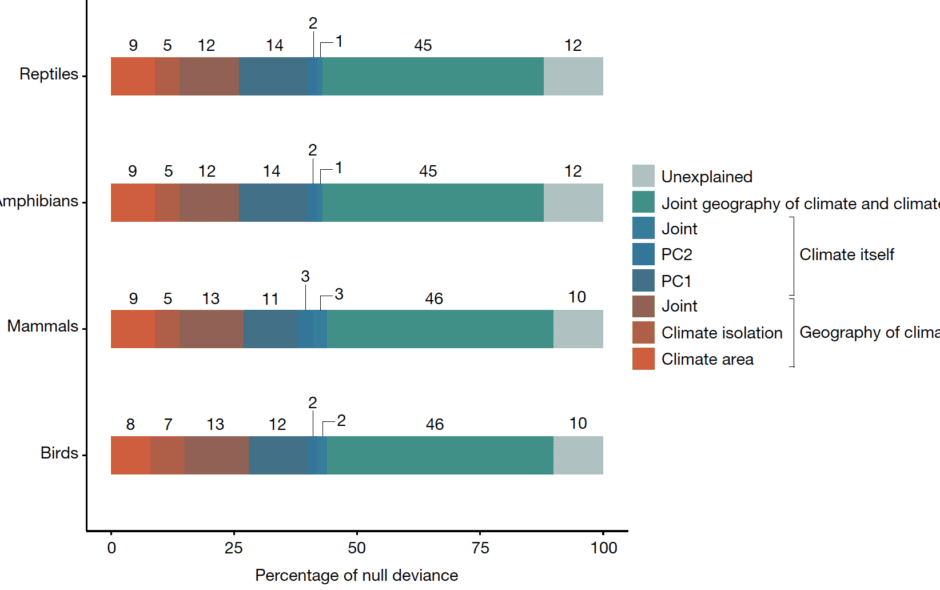
Ecological and evolutionary questions addressing diversity-environment relationships have been evaluated almost entirely in geographic space, yet most hypotheses are formulated in terms of environmental conditions. Recent examples evaluating macroecological patterns directly in environmental space suggest that such refocusing provides different perspectives on the mechanisms driving broad-scale patterns of diversity. Yet, we lack both conceptual frameworks and targeted studies to fully evaluate the potential contribution of such a refocus. Here, we focus on the concept of environmental space by briefly reviewing its use in ecology and evolution and suggesting avenues for further development. We encourage a re-evaluation of hypotheses and frameworks that have dominated ecological theory since the foundations of ecology with a very simple shift in the lens, that is, from geographical to environmental space. Focusing on environmental space also provides a crucial lens for climate change research, enabling a comprehensive evaluation of biodiversity dynamics and offering a holistic view of the interplay between species and their evolving environments. This shift enhances our ability to predict and adapt to future changes, enriching our understanding of biodiversity beyond more commonly done geographic analyses. Additionally, it aligns with the broader discourse on Biodiversity Patterns Redefined in Environmental Space.
https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.70008